Table Of Content

Asyou read, please refer the words in bold to the Basic Hair Structure and Hair Follicle diagrams below. Some parts of the Hair Follicle Diagram are also color-coded to highlight their importance. Your hair’s appearance is determined partly by the shape of your hair. If your hair has a circular circumference, it will be straight. As you get older, your hair can change color, texture, and thickness. It can even change some of its location, with too much in some areas and too little in others.
Hair and follicle morphology
Medulla is located in the center of the hair shaft preferably presented in coarser fibers. The outer covering of the hair shaft, the cuticle, is the protective outer layer of the hair. It is made up of cells that tile over each other partially overlapping. This is what both protects the cortex and holds the rope like cells together. A healthy cuticle layer is what gives hair its natural shiny appearance.
Hairs of other different animals
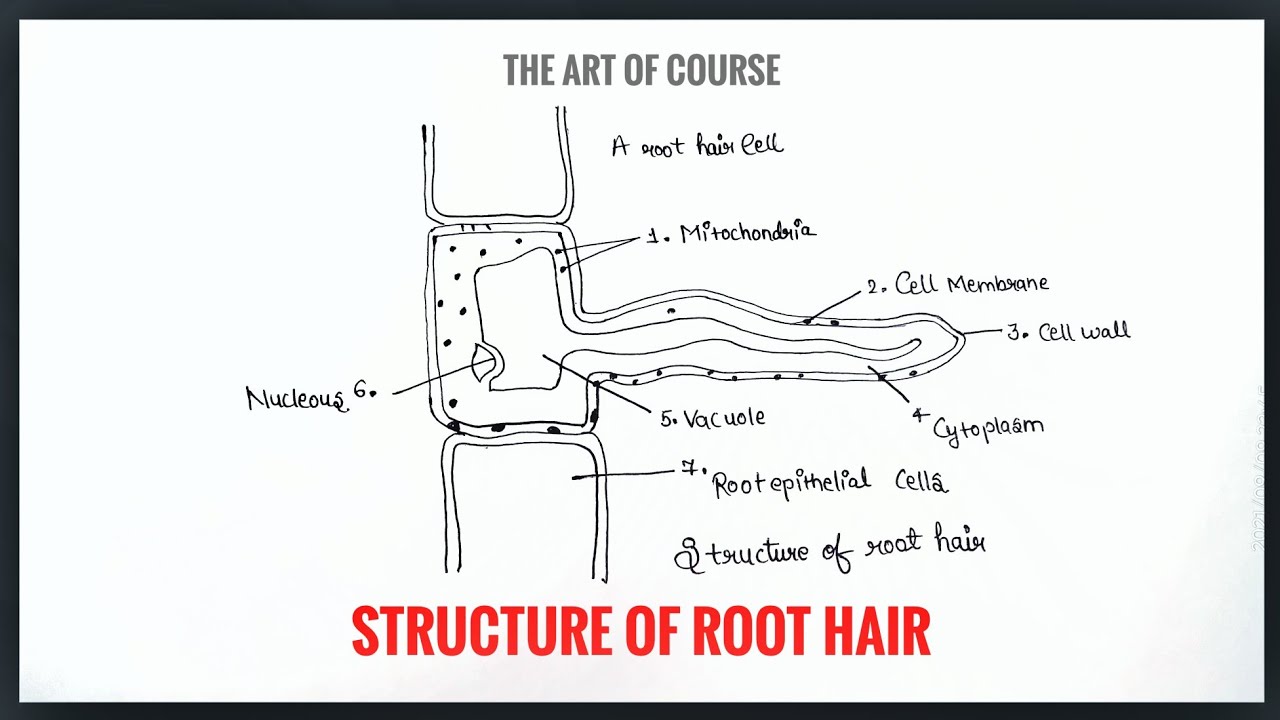
You will find two main parts in hair – a cylindrical shaft and a terminal hair follicle. This article might help you to know the different features of a hair (shaft and follicle) under a light microscope with their concise description. Again, I will try to show you the hairs of different animals like rabbits, cats, and dogs with their specific features. The hair follicle serves as a reservoir for epithelial and melanocyte stem cells and it is capable of being one of the few immune privileged sites of human body.
Anatomy, Hair
The hair follicle becomes almost verticle relative to the skin surface of any animal. Again, the skin surface overlying the attachment of the arrector pili muscle becomes depressed while the surrounding area becomes raised. Fine, let’s know some of the important microscopic features of these two structures (sebaceous gland and arrector pili muscle) from the skin histology slide.
The hair shaft is the visible, nongrowing portion of a hair protruding from the skin. In contrast to the continuous melanogenesis observed in epidermal melanocytes, follicular melanogenesis is a cyclic phenomenon. It is ceased in early the anagen-catagen transition, restarted with the down-regulation of key enzymes of melanogenesis, followed by hair follicle melanocyte apoptosis. The hair follicle is one of the characteristic features of mammals serves as a unique miniorgan (Figure 1).
The cuticle is composed of multiple layers of very thin, scaly cells that overlap each other like roof shingles with their free edges directed upward. The density of hair does not differ much from one person to another or even between the sexes; indeed, it is virtually the same in humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas. Differences in apparent hairiness are due mainly to differences in texture and pigmentation. And this, of course, only adds to the complexity thispuzzling type of hair loss presents. You can help keep your hair healthy by taking care of your overall health.
At the base of the hair bulb, the germinatinglayer merges into the outer root sheath(which forms the inner wall of the follicle). Hair is continually shed and renewed by the operation of alternating cycles of growth, rest, fallout, and renewed growth. The average life of different varieties of hair varies from about four months for downy hairs to three to five years for long scalp hairs. Now, let’s see the second diagram (schematic presentation), where the different layers of the hair follicle are seen.
The CDC Has a Shockingly Robust Vocabulary for Facial Hairstyles - GQ
The CDC Has a Shockingly Robust Vocabulary for Facial Hairstyles.
Posted: Wed, 26 Feb 2020 08:00:00 GMT [source]
You may determine the hair from the different parts of the animal’s body. The length, shape, size, color, stiffness, curliness, and microscopic features might help you to identify the hairs from the different body areas. Sometimes sebaceous gland occurs independently in the hair follicle and directly opens on the skin surface. The lipid of these inner cells is discharged by the disintegration of the innermost cells that are replaced by the proliferation of the outer cells. You will find the oily secretion from the sebaceous gland of any animal that helps to keep the skin and hair soft. Sometimes, a microscopic view shows the great mitotic activities of the hair root and bulb cells.
Cells lining the hair follicle are like shingles facing in the opposite direction. They interlock with the scales of the hair cuticle and resist pulling on the hair. When a hair is pulled out, this layer of follicle cells comes with it. It consists of several layers of elongated keratinized cells that appear cuboidal to flattened in cross sections.
Without enough niacin, follicles may not produce hair efficiently. The sebaceous gland produces sebum, or oil, which is the body’s natural conditioner. More sebum is produced during puberty, which is why acne is common during the teen years. It protects your skin and traps particles like dust around your eyes and ears. If your hair gets damaged, it can renew itself without scarring. The medulla of the dog hair is generally continuous, but it may be vacuolated to amorphous and occasionally very broad.
Again, the diagram shows the cortex layer just deep into the cuticle layer. The medulla of the hair is the core, which is also shown in this diagram. In addition, you will understand the medulla feature clearly from the next labeled diagram.
No comments:
Post a Comment