Table Of Content
Hair follicle development is related to the interactions between epithelial and mesenchymal cells. Many genes play substantial role in this interaction and also in hair follicle cycling [3–5]. Androgenetic alopecia is the most common presenting hair concern and affects 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States alone. Studies estimate that 70% of men and 40% of women are affected by androgenetic alopecia.
Hair Growth

The Hair Diagram® is the parent brand of Bold Hold lace adhesives and other temporary hold products along with the Ashley Marie Collection a phenomenal haircare line. Hi, I am Sonnet (veterinarian; I Completed my DVM – DOCTOR OF VETERINARY MEDICINE and have a good Knowledge of VETERINARY ANATOMY) from AnatomyLearner.com. I love sharing essential and informative veterinary anatomy topics with the new learner.
5. Immunology of hair follicle
How much of each hair type you have varies from person to person and also depends on your age and sex. About 30 percent of the body’s surface is covered with terminal hair in women, compared to about 90 percent in men. I have already described how to visualize the hairs under a light microscope easily. The scales of the cat’s hair cuticles are spinous and very prominent.
Structure of hair follicle under a microscope
Mullets Are Making a Comeback — How to Grow a Modern Mullet 2021 - Men's Health
Mullets Are Making a Comeback — How to Grow a Modern Mullet 2021.
Posted: Wed, 13 Jan 2021 08:00:00 GMT [source]
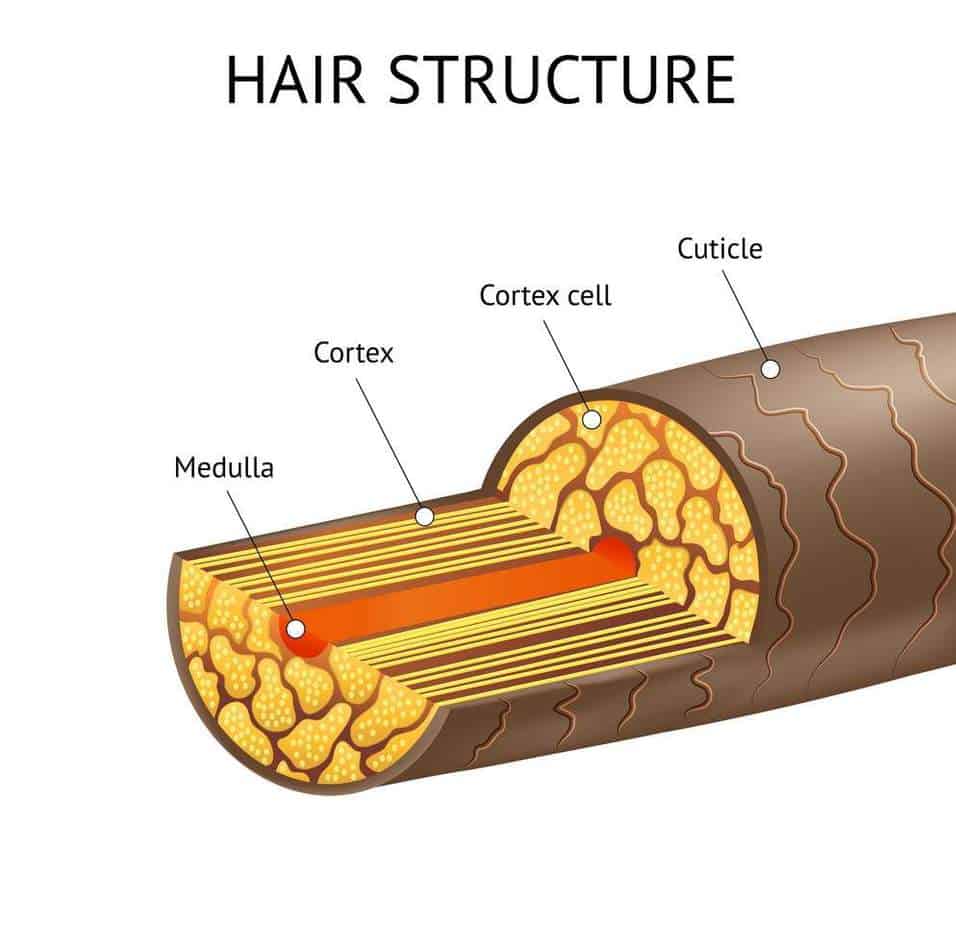
Again, it may appear white or translucent in transmitting lights. Even you may find double medulla in the hairs of some animal species. The medulla contains the pigment granules, though some species have no pigment granules in their hairs.
Again, the microscopic figure of the inner root layer shows one to three layers of flattened nucleated cells. These flattened nucleated cells from the Huxley’s layer or the stratum epitheliale granuloferum. You will find the large eosinophilic granules in the cytoplasm of these flattened nucleated cells of the Huxley’s layer. You will find these spinous scales in the hairs of animals like dogs, cats, and money.
Fiber length is often dependent on the duration of the anagen or actively growing phase of the follicle [17]. The featured regulatory proteins in anagen phase are BMPs, sonic hedgehog, several WNT proteins and receptors. Hair is a slender filament of keratinized cells that grows from an oblique tube in the skin called a hair follicle. Each hair is composed of columns of dead, keratinized epidermal cells bonded together by extracellular proteins. The hair shaft is the superficial portion of the hair, which projects above the surface of the skin. The hair root is the portion of the hair deep to the shaft that penetrates into the dermis, and sometimes into the subcutaneous layer.
In brief: What is the structure of hair and how does it grow?
In this outer layer of the hair follicle, you will find the round and nucleated cells. You will find the overlapping scales with a narrow margin in the imbricate or flattened scales of animals and humans. The diagram shows the imbricate pattern of the cuticle scales from human hair. So, hair is an epidermal down growth embedded into the dermis or hypodermis of the animal’s skin.
There are about 5 million hairs on the human body, and 98 percent of them are on the general body surface, not the head. Hairs are nonliving structures that form in organs called hair follicles. Each strand of hair grows from a root located in the base of the hair follicle, which is composed of keratin cells.
Hair identifying characteristics in a microscope
In humans, hair has various functions such as protection against external factors, sebum, apocrine sweat and pheromones production and thermoregulation. The hair also plays important roles for the individual’s social and sexual interaction [1, 2]. Keratin is a special protein, which is resistant to wear and tear. Like other proteins in the body, keratin is also a large molecule made up of smaller units called amino acids.
Hair follicles extend deep into the dermis, often projecting into the underlying subcutaneous layer. The epithelium at the follicle base surrounds a small hair papilla, a peg of connective tissue containing capillaries and nerves. The hair bulb consists of epithelial cells that surround the papilla.
When the cuticle is damaged or destroyed the medulla is unable to maintain its moisture homeostasis and suffers from dehydration. In the damage state in addition to dry hair, the medulla is more prone to damage from the environmental agents and chemicals. The root begins at the hair bulb and extends distally to the point where the internal organization of the hair is complete, about halfway to the skin surface. The hair shaft extends from this halfway point to the skin surface, where we see the exposed hair tip.
Furthermore, the hair pigment, melanin, is a potent free-radical scavenger. Melanin production inside the active anagen hair bulb may, therefore, help to buffer cell stress induced by reactive oxygen species. This can occur on the entire scalp (alopecia totalis) or body (alopecia universalis) or may be localized to specific areas (alopecia areata). Alopecia areata can progress to alopecia totalis and often begins acutely and spreads gradually over the course of weeks to months. Alopecia is an autoimmune disease mediated by T lymphocytes and other immune cells.
The pigment granules are occasionally coarse and distributed into the root of the hair. Again, the outer layer of the inner root shows a single layer of cuboidal cells with flattened nuclei. This layer is the Henle’s layer or the stratum epitheliale pallidum. Write the microscope features of these hairs sample so that you may compare them to each other. The medulla’s cornified element contains melanin responsible for the color of hair.
Again, in the labeled diagram, you will see the longitudinal section of the spinous or petal-like scales of the cuticle from animal’s hair. It is made of scales that overlap and protect the inner layer of hair. These scales point from the proximal end to the distal end of the hair shaft. So, the cuticle is a thin external membrane that covers the surface of the hair shaft. You will find flattened cornified cells in the cuticle structure under the microscope.
Below the epidermis is the dermis.The dermis is the thickest part of the skin and contains blood vesselsto supply the nutrients needed for skin cells to grow. The most important function of hair in mammals is that of insulating against cold by conserving body heat. The differing colours and colour patterns in hair coats can also serve purposes of camouflage and of sexual recognition and attraction among the members of a species.
No comments:
Post a Comment